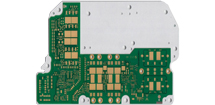
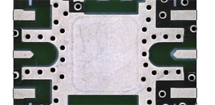
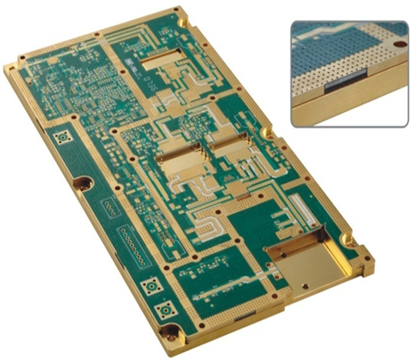
Heat Sink PCB
Heat Sink PCBs are a special type of printed circuit board with a heat-dissipating metal core that integrates heat dissipation functionality, bonding copper or aluminum-based metal components to specific areas of the circuit board that require cooling, with heat being dissipated through the metal parts, thereby enhancing the overall thermal performance of the PCB and providing an optimal thermal management solution for high-power or high-performance electronic devices. Heat Sink PCBs are designed to enhance thermal management by integrating metal components like copper or aluminum onto the PCB surface. These metal parts efficiently absorb and dissipate heat from high-performance electronic components, ensuring optimal operating temperatures. The metal layers can be customized in thickness, size, and placement to meet specific thermal needs, making Heat Sink PCBs versatile and effective in various applications. Heat Sink PCBs are commonly used in high-power electronics, LED lighting, power supplies, automotive electronics, and telecommunications equipment. They prevent overheating, extending component lifespan and improving efficiency. By integrating heat dissipation directly into the PCB, they eliminate the need for additional cooling solutions, offering a more compact and cost-effective alternative to traditional heat sinks. Key Features of Heat Sink PCB : |
 |
|
 |
1, Enhanced thermal dissipation: The integration of a heat sink directly into the PCB design allows for better heat dissipation from electronic components, helping to prevent overheating and improve overall system performance. 2, Compact design: Heat sink PCBs help to save space by integrating thermal management solutions directly into the board, eliminating the need for additional heat sinks or cooling mechanisms. 3, Improved reliability: By effectively managing heat, heat sink PCBs can help increase the lifespan and reliability of electronic components by preventing thermal issues that can lead to premature failure. 4, Cost-effective solution: Heat sink PCBs can provide a cost-effective thermal management solution by eliminating the need for separate heat sinks, reducing assembly time. |
|
5, Customizable options: Heat sink PCBs can be customized to meet specific thermal requirements for different applications. |
||
Why Heat Sink PCBs Used For Thermal Management ? |
Heat Sink PCBs are used for thermal management because they help dissipate heat generated by electronic components. Here are some reasons why heat sink PCBs are commonly used: 1, Heat dissipation: Electronic components, especially high-power components like CPUs or power transistors, generate heat during operation. If the heat is not effectively dissipated, it can lead to performance degradation, premature component failure, or even a complete systems breakdown. Heat sink PCBs provide a larger surface area to dissipate heat and help maintain optimal operating temperatures. |
|
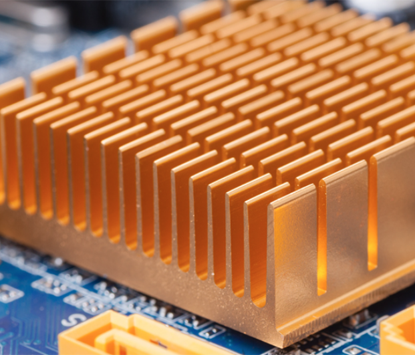 |
2, Improved reliability: By efficiently dissipating heat, heat sink PCBs help increase the reliability and lifespan of electronic devices. Excessive heat can cause wear and tear on components, degrade solder joints, and lead to thermal stress-related failures. Heat sink PCBs prevent heat buildup, thus reducing the risk of malfunctions and extending the lifespan of the components. 3, Compact design: Heat sink PCBs offer a compact solution for thermal management compared to traditional heat sinks. They integrate both the electronic circuitry and the heat dissipation function into a single component, eliminating the need for separate heat sink attachments or additional space on the board. This can be especially beneficial in space-constrained applications or when weight reduction is a priority. 4, Thermal conductivity: Heat sink PCBs are typically made from materials with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminum or copper. These materials conduct heat more efficiently than standard PCB materials, allowing for better heat transfer from the components to the heat sink. This helps in quickly removing heat from sensitive components and maintaining lower operating temperatures. |
5, Cost-effective: Integrating heat sink functionality into the PCB design can be cost-effective compared to using separate heat sinks or complex cooling systems. It reduces the number of components required, simplifies assembly processes, and can potentially lower manufacturing costs. Heat Sink PCBs are an effective solution for managing thermal issues in electronic devices, offering improved reliability, compact design, efficient heat dissipation, and cost-effectiveness. |
|
What Product Types Need To Consider Using Heat Sink PCB ? |
Various product types can benefit from using heat sink PCBs for thermal management. Here is a comprehensive overview of the product types that often require consideration for incorporating heat sink PCBs: 1, Consumer Electronics: Devices such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and gaming consoles often contain high-performance components like processors, graphics cards, and power management ICs that generate significant heat during operation. Heat sink PCBs can help dissipate this heat efficiently and prevent overheating issues. 2, Automotive Electronics: In vehicles, electronic components are exposed to harsh environmental conditions and temperature fluctuations. Heat sink PCBs can help manage the heat generated by components like power electronics, sensors, and infotainment systems, ensuring reliable performance in automotive applications. |
|
 |
3, LED Lighting: High-power LED lighting fixtures generate heat that can affect performance and longevity. Heat sink PCBs are commonly used in LED lighting applications to maintain optimal operating temperatures and extend the lifespan of the LEDs. 4, Industrial Equipment: Industrial machinery and equipment often have electronics that operate in demanding environments. Heat sink PCBs are essential for thermal management in industrial automation systems, motor drives, power supplies, and control panels, where heat dissipation is critical for reliable operation. 5, Telecommunications: Networking equipment, such as routers, switches, and base stations, can benefit from heat sink PCBs to regulate temperature and prevent heat-related failures. These devices often operate continuously at high speeds, leading to heat generation that needs to be effectively managed. 6, Medical Devices: Medical electronics, including imaging systems, patient monitoring devices, and diagnostic equipment, require stable and controlled temperatures for accurate operation. Heat sink PCBs help maintain the thermal balance in medical devices, ensuring reliability and performance consistency. |
7, Renewable Energy Systems: Solar inverters, wind turbine controllers, and other renewable energy systems contain sensitive electronics that must operate efficiently to maximize energy production. Heat sink PCBs play a crucial role in managing heat in these systems and maintaining their performance over time. 8, Aerospace and Defense: Electronic systems in aerospace and defense applications are subject to extreme temperatures and rugged conditions. Heat sink PCBs are essential for thermal management in avionics, radar systems, communication equipment, and military electronics to ensure operational reliability and longevity. A wide range of product types across various industries can benefit from using heat sink PCBs for effective thermal management and ensuring the reliable operation of electronic components. |
|
Advantages of Heat Sink PCB : |
|
1, Enhanced Thermal Management: Heat sink PCBs are designed to efficiently dissipate heat generated by electronic components. By effectively transferring heat away from sensitive components, they prevent overheating and ensure stable performance even under demanding conditions. 2, Improved Reliability: By maintaining lower operating temperatures, heat sink PCBs contribute to the overall reliability and longevity of electronic devices. They help minimize thermal stress on components, reducing the risk of premature failure and enhancing the overall lifespan of the device. |
|
 |
3, Optimized Performance: Effective heat dissipation provided by heat sink PCBs allows electronic devices to operate at optimal performance levels. By keeping temperatures in check, these PCBs prevent thermal throttling and ensure that components can function at their maximum capacity without being limited by excessive heat. 4, Space Efficiency: Integrating heat sink functionality directly into the PCB eliminates the need for separate heat sinks or cooling mechanisms. This compact design saves space within the device, enabling more efficient use of available real estate on the circuit board. It is especially beneficial in smaller form factor devices or applications where space is a constraint. 5, Cost-Effectiveness: Heat sink PCBs can be a cost-effective solution compared to traditional heat sink designs. By integrating the heat sink directly onto the circuit board, manufacturers can eliminate the need for additional components, assembly steps, and associated costs. This streamlined approach reduces manufacturing complexity and overall production expenses. |
6, Customization and Flexibility: Heat sink PCBs can be customized to meet specific thermal requirements of different electronic applications. Designers can optimize the layout, size, and shape of the heat sink to match the heat dissipation needs of the device. This flexibility allows for precise thermal management and ensures efficient cooling for various electronic components. 7, Ease of Integration: Heat sink PCBs can be seamlessly integrated into the existing manufacturing processes for circuit boards. They can be designed to fit standard PCB specifications, enabling manufacturers to incorporate heat sink functionality into their products without significant modifications or disruptions in the production line. Heat Sink PCBs provide improved thermal management, enhanced reliability, optimized performance, space efficiency, cost-effectiveness, customization options, and ease of integration. These advantages make them a valuable solution for managing heat-related challenges in electronic devices. |
|
Manufacturing Challenges of Heat Sink PCB : |
Manufacturing heat sink PCBs presents several unique challenges due to the integration of thermal management features into the circuit board. Some of the key manufacturing challenges include: 1, Material Selection: Choosing the right materials for the PCB substrate and the heat sink itself is crucial. The materials need to have excellent thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and compatibility with standard PCB manufacturing processes. Finding materials that meet these requirements while remaining cost-effective can be a challenge. |
|
 |
2, Design Complexity: Integrating heat sink features into a PCB design adds an extra layer of complexity. Designers need to ensure that the heat sink layout does not interfere with the functionality of other components on the board. This requires careful planning and often involves iterative testing and refinement to optimize the design. 3, Thermal Interface Materials: Properly integrating the thermal interface materials between the electronic components and the heat sink is essential for efficient heat dissipation. Ensuring consistent application of these materials during manufacturing, especially in high-volume production, can be challenging. 4, Manufacturability: Fabricating PCBs with integrated heat sinks requires specialized manufacturing techniques. Processes such as embedding heat pipes, vapor chambers, or other heat transfer structures into the PCB substrate may require additional equipment and expertise, adding to the manufacturing complexity. |
5, Quality Control: Verifying the effectiveness of the heat sink integration and the overall thermal performance of the PCBs is critical. Implementing quality control measures to test the thermal characteristics of each PCB unit can be time-consuming and may require specialized testing equipment. 6, Cost Considerations: The integration of heat sink features into the PCB adds to the overall manufacturing cost. Balancing the benefits of improved thermal management with the additional manufacturing expenses can be a challenge for manufacturers seeking to offer competitive pricing. 7, Scalability: Adapting the manufacturing process for heat sink PCBs to accommodate varying production volumes can be a challenge. The processes and techniques used for prototyping and low-volume production may not always scale easily to high-volume manufacturing. Addressing these challenges requires collaboration between PCB designers, materials specialists, and manufacturing engineers to develop efficient and cost-effective processes for integrating heat sink functionality into PCBs while ensuring reliability and performance. Overcoming these challenges is essential for harnessing the benefits of heat sink PCBs in a wide range of electronic applications. |
|
Material Types of Heat Sink PCB : |
1, Aluminum Heat Sink PCB : 2, Copper Heat Sink PCB : 3, Pinned Heat Sink PCB : 4, Finned Heat Sink PCB : |
Process Types of Heat Sink PCB : |
 |
1, Stamped Heat Sink PCB: 2, Bonded Heat Sink PCB : 3, Skived Heat Sink PCB : 4, Swaged Heat Sink PCB : |
5, Forged Heat Sink PCB : 6, Machining Heat Sink PCB : |
|
Technology Capabilities of Heat Sink PCB : |
|
1, Post Bonding Technologies(Coin inside,Press fit technology). 2, Pre-bonding (Copper or aluminum based). 3, Sweat Soldering (Based metal sweat soldering). 4, Step Slot technology. 5, Copper and Silver Filled Technology, Thermal Management.
|