High Voltage Divider Resistors
High Voltage Divider Resistors, also called High Voltage Divider Ceramic Resistors, are passive components employed in circuits to step down voltage levels through a series of resistors, with the primary function of lowering the input voltage to a stable and predictable output, typically a fraction of the input, which is especially vital in high-voltage applications where they reduce high voltages to safer levels for measurement or other purposes.
High Voltage Divider Resistors are specialized electronic components designed to accurately measure or step down high voltage levels to a more manageable range for measurement or signal processing. These resistors are typically arranged in a series, forming a voltage-dividing network. Often based on a ceramic substrate and utilizing thick-film technology, they offer precise, stable, and uniform resistance values that can withstand high voltages without degradation. The use of ceramic substrates enhances their ability to endure high voltages, ensuring long-term reliability and stability.
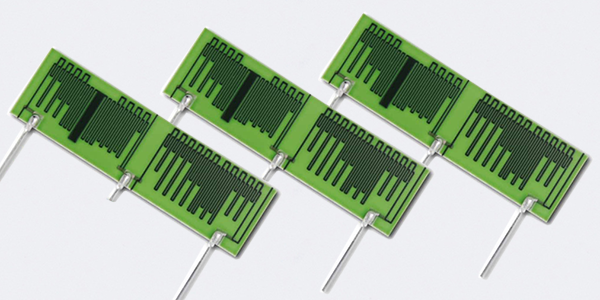
High Voltage Divider Ceramic Resistors are widely used in high-voltage measurement, instrumentation, and signal processing applications. They are commonly employed in scenarios that require stepping down high-voltage signals to lower voltages for safe measurement, such as in power systems, industrial control devices, and scientific experiments. By using a voltage divider resistor, a stable and adjustable low voltage output can be provided in high-voltage environments, suitable for analysis, monitoring, or further processing. Additionally, they are used in voltage monitoring in power systems and electrical equipment testing, ensuring safety and reliability during operations.
Advantages of High Voltage Divider Resistors :
● High Voltage Capability: High Voltage Divider Resistors are engineered to handle and accurately divide very high voltage levels, which makes them suitable for applications such as power transmission testing, high voltage power supplies, and medical equipment.
● Stability: The use of ceramic substrates and thick-film technology results in resistors with low temperature coefficients, ensuring that the resistance value remains consistent across a wide range of temperatures.
● Precision: High Voltage Divider Resistors can be manufactured with very tight tolerances, contributing to the overall accuracy of the voltage division ratio.
● Reliability: The robust construction of ceramic-based high voltage dividers lends itself to long-term reliability and a long service life.
● Insulation Properties: Ceramic is an excellent insulating material, which helps prevent flashovers and provides good dielectric strength.
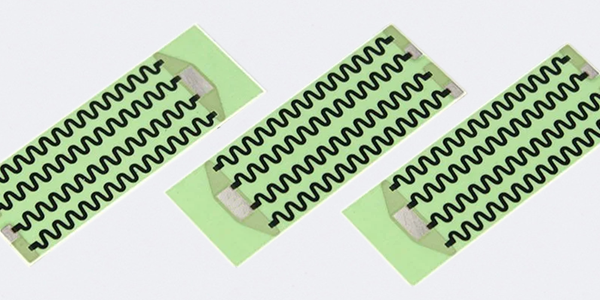
● Customizability: High Voltage Divider Resistors can be custom-designed to meet specific application requirements, including resistance values, voltage ratings, and physical dimensions.
● Noise Immunity: The materials and construction of high voltage dividers often provide inherent noise immunity, ensuring that the output signal is not corrupted by electrical interference.
● Safety: By reducing high voltages to safer levels for measurement, high voltage dividers enhance the safety of both the equipment and the personnel using it.
● Long-term Stability: Unlike some other types of resistors, high voltage dividers based on ceramic and thick-film technology do not exhibit significant aging effects, maintaining their performance over time.
● Versatility: High Voltage Divider Resistors can be used in a variety of applications, from scientific research to industrial processes, where high voltage measurement accuracy is critical.
High Voltage Divider Resistors are essential components in high voltage measurement and monitoring systems, providing a reliable and accurate means of voltage attenuation and measurement.
Applications of High Voltage Divider Resistors :
● Voltage Measurement and Monitoring: High Voltage Divider Resistors are commonly used in applications that require the measurement of high voltages, such as power transmission testing and monitoring the operation of electrical systems .
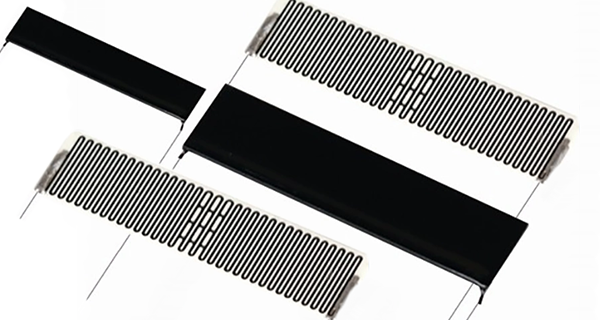
● Voltage Regulation: High Voltage Divider Resistors are utilized in voltage regulators for applications such as DC-DC converters and linear regulators to set the output voltage through the ratio R2/(R1+R2), where R1 and R2 are the resistors in the divider network .
● Calibration Equipment: In metrology, High Voltage Divider Resistors are essential for calibrating high voltage measurements against national reference standards, often based on the Josephson effect, which is limited to less than 10 V. These dividers are used to transfer reference voltages up to several hundred kilovolts .
● Medical Equipment: High Voltage Divider Resistors are used in medical devices such as X-ray machines and CAT scanners, where high voltages are required for imaging purposes, and accurate voltage division is necessary for stable operation .
● Industrial Control Systems: In heavy industrial applications, these resistors are used in motor drives and power supplies to ensure precise control of high voltages .
● Automotive Applications: High Voltage Divider Resistors are used in electric vehicles for high voltage DC/DC converters and inverters, where they help maintain the stability and accuracy of the electrical system .
● High Voltage Experiments: High Voltage Divider Resistors are also used in scientific research and experiments that involve high voltages, such as gas discharge studies, where they can safely step down voltages for controlled experimental conditions .
● Precision Resistors for Feedback Networks: In applications requiring high precision and low temperature coefficients, such as in feedback networks for voltage references or amplifiers, high voltage divider resistors provide the necessary stability and accuracy .
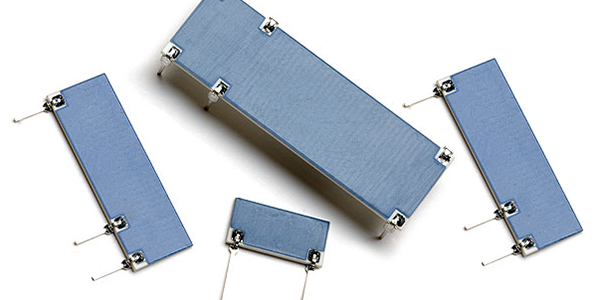
● Power Supplies: High Voltage Divider Resistors are used in power supplies to provide reference voltages for operation and to ensure the output voltage meets the required specifications .
Manufacturing of High Voltage Divider Ceramic Resistors :
Voltage Divider Network Resistors are manufactured through a precise and specialized process that involves the integration of carefully selected materials and advanced thick-film technology.
● Ceramic Substrate: The foundation of a high voltage divider ceramic resistor is a ceramic substrate. Ceramic materials are chosen for their excellent insulating properties, high-temperature stability, and their ability to withstand high voltages without dielectric breakdown.
● Conductive Paste: The resistive element is created using a thick-film paste that typically consists of a mixture of conductive materials, such as metal oxides or metal particles, and an organic vehicle that acts as a binder. Common conductive materials include ruthenium dioxide, tin oxide, or nickel.
● Screen Printing: The conductive paste is screen-printed onto the ceramic substrate in a pattern that defines the resistive tracks and terminations. This process ensures that the paste is applied accurately and uniformly across the substrate.

● Firing Process: After printing, the substrate with the applied paste undergoes a firing process in a controlled atmosphere furnace. This step burns off the organic components of the paste and sintered the conductive particles, resulting in a durable and conductive path.
● Laser Trimming: To achieve the desired resistance value with high precision, laser trimming is often employed. A focused laser beam removes a precise amount of the resistive material, adjusting the resistance value without affecting the surrounding area.
● Coating: After the firing process, a protective and insulating coating may be applied to the resistor. This can be a glass or polymer coating that provides environmental protection and enhances the stability of the resistor.
● Terminal Attachment: The final step involves attaching terminals to the resistor, which can be done through soldering, welding, or conductive adhesives. These terminals provide a means to connect the resistor within a circuit.
● Quality Control and Testing: Throughout the manufacturing process, rigorous quality control checks are performed to ensure that each resistor meets the required specifications. This includes testing for resistance value, temperature coefficient, voltage coefficient, and insulation resistance.
● Matching Process: For high-precision applications, resistors may undergo a matching process where pairs of resistors with closely matched characteristics are selected to ensure the stability of the voltage division ratio over a range of operating conditions.

High Voltage Divider Ceramic Resistors are produced through a highly controlled and precise manufacturing process to ensure the creation of reliable components capable of operating in demanding high voltage environments.
Accuracy and Stability of High Voltage Divider Resistors :
● Precise Resistance Values: High Voltage Divider Resistors are manufactured with very tight tolerances, ensuring that the resistance values are accurate and consistent. This precision is critical for maintaining the correct voltage ratio.
● Temperature Stability: High Voltage Divider Resistors used in high voltage dividers are often made from materials with low temperature coefficients of resistance (TCR). This means that their resistance values change very little with temperature, which is crucial for maintaining stability across a wide range of operating conditions.
● Matching: In a voltage divider, the ratio of the output voltage to the input voltage is determined by the ratio of the two resistors. If these resistors are well-matched, the divider will maintain a consistent output voltage regardless of the input voltage.
● Immunity to Noise: High Voltage Divider Resistors are often designed to minimize noise pickup. This can be achieved through careful layout and shielding, ensuring that the output voltage is not affected by electrical interference.
● Linearity: High Voltage Divider Resistors in a high voltage divider are typically linear, meaning that their resistance does not change with the applied voltage. This is important for maintaining a consistent voltage ratio across the operating range of the divider.

● Low Leakage Current: High Voltage Divider Resistors are designed to have low leakage currents, which helps to maintain the stability of the output voltage. Leakage current can introduce errors in the output voltage, especially at high voltages.
● Physical Construction: The physical layout of the resistors in a high voltage divider can affect its performance. Proper layout can minimize the impact of parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can introduce errors in the output voltage.
● Calibration: High Voltage Divider Resistors are calibrated during manufacturing to ensure that they meet the required accuracy specifications. This calibration process can involve adjusting the resistor values to achieve the desired voltage ratio.
● Protection Features: High Voltage Divider Resistors include protection features such as overvoltage protection, which can help to maintain the stability of the output voltage by preventing damage to the divider from excessive voltage spikes.
● Isolation: In some applications, High Voltage Divider Resistors may be isolated from the high voltage source, which can reduce the impact of source voltage fluctuations on the divider's output.
By incorporating these design features, High Voltage Divider Resistors can provide a stable and accurate reference voltage that is essential for high precision measurement and testing applications.
For more information, Please refer to Thick Film Ceramic Resistors.
Custom Thick Film Resistors
- Custom Thick Film Resistor Elements
- High Voltage Ceramic Resistors
- High Value Ceramic Resistors
- High Energy Ceramic Resistors
- High Power Ceramic Resistors
- Humidity Sensitive Ceramic Resistors
- Thick Film Non-Inductive Resistors
- Thick Film Planar Resistors
- Thick Film Tubular Resistors
- Thick Film Resistor Networks
- Thick Film Surge Resistors
- Radio Frequency Power Resistors
- High Voltage Divider Resistors
- Ceramic Variable Resistors
